首先我们回想一下注册杂项设备的三大流程,我们在 Windows 上面新建 misc.c 文件,并用 sourceinsight打开。我们可以将上次编写的 helloworld.c 里面的代码拷贝到 misc.c 文件,并修改为如下图所示:

添加头文件
/*注册杂项设备头文件*/
#include
/*注册设备节点的文件结构体*/
#include
填充 miscdevice 结构体
struct miscdevice misc_dev = {
.minor = MISC_DYNAMIC_MINOR, .name = "hello_misc", .fops = &misc_fops, };
上述代码第 2 行的 minor 为 MISC_DYNAMIC_MINOR,miscdevice 核心层会自动找一个空闲的次设备号,
否则用 minor 指定的次设备号。上述代码第 3 行 name 是设备的名称,我们自定义为"hello_misc" 填充 file_operations 结构体
struct file_operations misc_fops={
.owner = THIS_MODULE
};
THIS_MODULE 宏是什么意思呢?它在 include/linux/module.h 里的定义是
#define THIS_MODULE (&__this_module)
它是一个 struct module 变量,代表当前模块,可以通过 THIS_MODULE 宏来引用模块的 struct module
结构,比如使用 THIS_MODULE->state 可以获得当前模块的状态。这个 owner 指针指向的就是你的模块。注册杂项设备并生成设备节点
在 misc_init()函数中填充 misc_register()函数注册杂项设备,并判断杂项设备是否注册成功。
static int misc_init(void){
int ret;
ret = misc_register(&misc_dev); //注册杂项设备
if(ret<0) //判断杂项设备是否注册成功
{
printk("misc registe is error "); //打印杂项设备注册失败
}
printk("misc registe is succeed "); //打印杂项设备注册成功
return 0;
}
在 misc_exit()函数中填充 misc_deregister()函数注销杂项设备。
static void misc_exit(void){
misc_deregister(&misc_dev); //注销杂项设备
printk("misc gooodbye! "); //打印杂项设备注销成功
}
完整的代码如下图所示:
/*
* @Descripttion: 最简单的杂项设备驱动
* @version:
* @Author: topeet
*/
#include //初始化头文件
#include //最基本的文件,支持动态添加和卸载模块。
#include /*注册杂项设备头文件*/
#include /*注册设备节点的文件结构体*/
struct file_operations misc_fops={ //文件操作集
.owner = THIS_MODULE
};
struct miscdevice misc_dev = { //杂项设备结构体
.minor = MISC_DYNAMIC_MINOR, //动态申请的次设备号
.name = "hello_misc", //杂项设备名字是 hello_misc
.fops = &misc_fops, //文件操作集
};
static int misc_init(void){ //在初始化函数中注册杂项设备
int ret;
ret = misc_register(&misc_dev);
if(ret<0)
{
printk("misc registe is error ");
}
printk("misc registe is succeed ");
return 0;
}
static void misc_exit(void) { //在卸载函数中注销杂项设备
misc_deregister(&misc_dev);
printk(" misc gooodbye! ");
}
module_init(misc_init);
module_exit(misc_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
现在最简单的杂项设备的驱动就写完了,那么接下来我们可以把这个驱动编译一下,然后放到我们的开发板上面运行。我们编译驱动,可以将它编译进内核里面,也可以将它编译成模块。
2 编译驱动程序
这里我们以 imx6ull 开发板为例,将杂项设备驱动编译成模块,请参考本手册第三十九章 Linux 内核模
块。我们将 misc.c 文件拷贝到 Ubuntu 的/home/topeet/driver/imx6ull/misc 目录下。将上次编译 helloworld
的 Makefile 文件拷贝到 misc.c 同级目录下,修改 Makefile 为:
obj-m += misc.o #先写生成的中间文件的名字是什么,-m 的意思是把我们的驱动编译成模块
KDIR:=/home/topeet/driver/imx6ull/linux-imx-rel_imx_4.1.15_2.1.0_ga/
PWD?=$(shell pwd) #获取当前目录的变量
all:
make -C $(KDIR) M=$(PWD) modules #make 会进入内核源码的路径,然后把当前路径下的代码编译成模块
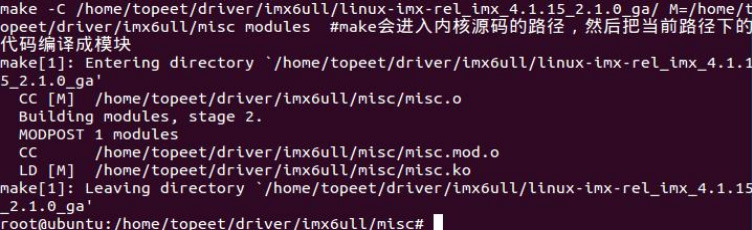
驱动编译成功生成了 ko 文件,如下图所示:
3 运行测试
启动 imx6ull 开发板,我们通过 nfs 挂载共享文件目录,注意!nfs 的配置和使用,请参考本手册第三十
七章 37.2.3 搭建nfs 共享目录章节配置。
我们进入到共享目录,加载驱动模块如图所示:
cd imx6ull/
ls
cd misc/
insmod misc.ko
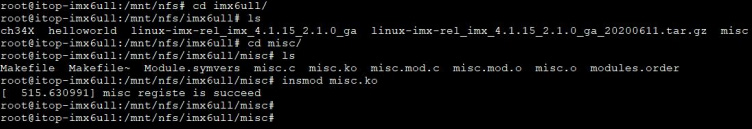
驱动加载成功后,输入以下命令,查看注册的设备节点是否存在,如下图所示,设备节点存在。
ls /dev/h*

我们输入以下命令拆卸驱动模块,如下图所示:
rmmod misc

那么,现在最简单的杂项设备已经完成了。

本文摘自 :https://blog.51cto.com/u

 开通会员
开通会员